Banking System Simulator
An interactive command-driven banking system demonstrating object-oriented design, design patterns, and test-driven development
Quick Start
Click on an example scenario to see pre-built banking operations
Type commands directly with autocomplete and syntax help
Click on accounts to view transaction history and details
Banking System Simulator
Interactive command-driven banking system
Example Scenarios
Pre-built demos to explore banking features
No Accounts Yet
Create your first account using the terminal or try an example scenario
create checking 12345678 1.0System Architecture
UML Class Diagram
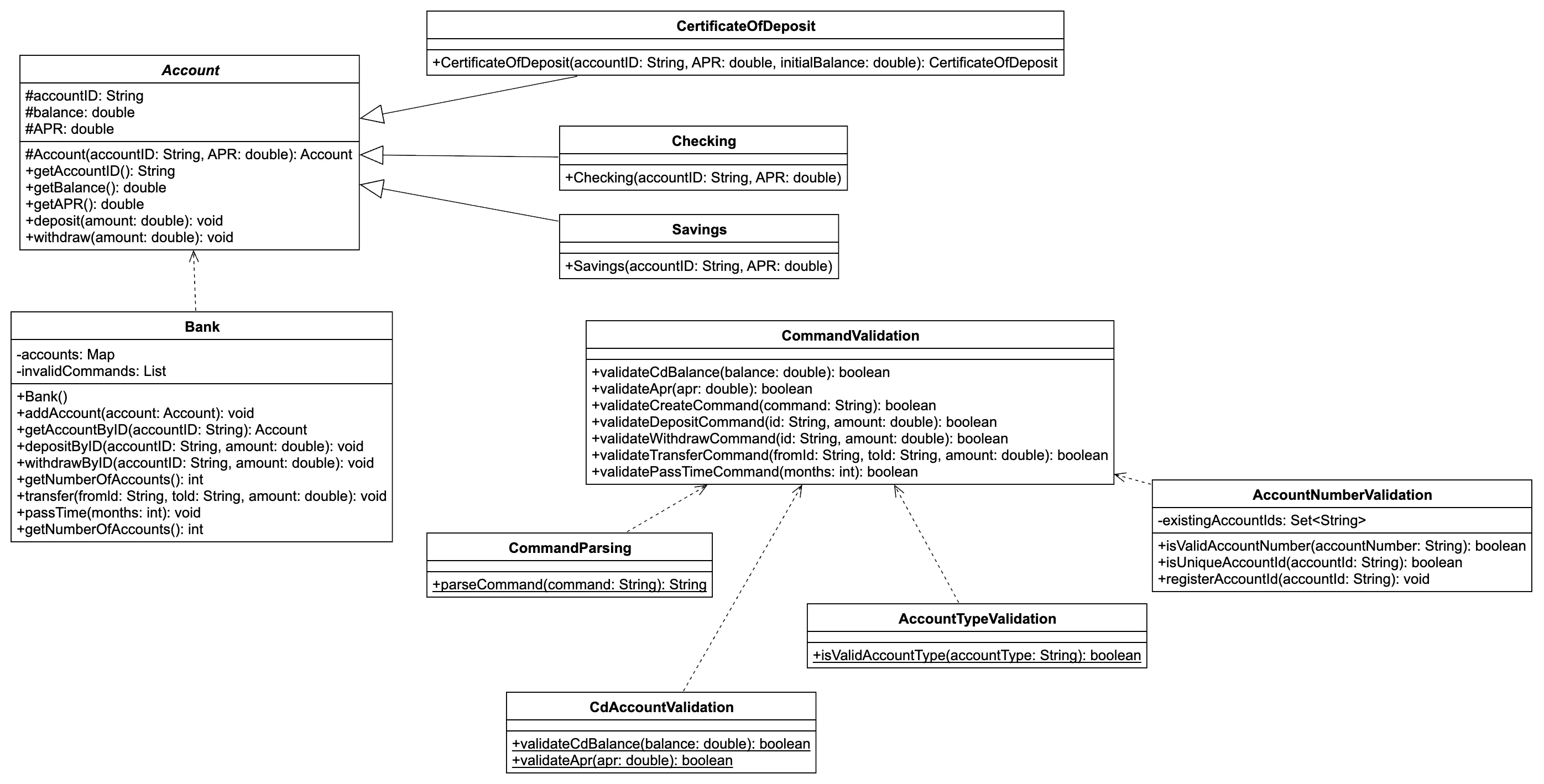
Component Flow
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ MasterControl │
│ (Orchestrates command processing pipeline) │
└────────────────┬────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
┌───────┴────────┬──────────────┬─────────────┐
│ │ │ │
┌────▼─────┐ ┌─────▼─────┐ ┌─────▼──┐ ┌───────▼──────┐
│ Command │ │ Command │ │ Bank │ │ Transaction │
│Validation│ │ Processor │ │(Repo) │ │ Logger │
└──────────┘ └───────────┘ └───┬────┘ └──────────────┘
│
┌─────────┼──────────┐
│ │ │
┌────▼───┐ ┌───▼────┐ ┌───▼───┐
│Checking│ │Savings │ │ CD │
│Account │ │Account │ │Account│
└────────┘ └────────┘ └───────┘MasterControl
Central coordinator that processes command lists, validates each command through validators, executes valid commands via processors, and generates formatted output with account states and transaction history.
Command Pattern
Separation of command validation and execution allows for extensibility, maintainability, and adherence to the Single Responsibility Principle. Each validator and processor handles one specific command type.
Bank (Repository)
Manages account storage using a Map data structure for O(1) lookups by account ID, handles time passage logic including APR accrual and fee deductions, and enforces business rules like zero-balance removal.
Account Hierarchy
Polymorphic design with an abstract Account base class and specialized subclasses (Checking, Savings, CD) that inherit common behavior while implementing type-specific features like CD's quarterly APR compounding.
Command Processing Flow
- 1User submits command string (e.g., "create checking 12345678 1.5")
- 2CommandValidation parses and validates command syntax and business rules
- 3If valid, CommandProcessor executes the operation on the Bank
- 4TransactionLogger records the command for audit trail
- 5MasterControl generates formatted output with account states and transactions
Design Patterns
Industry-standard software design patterns applied to real-world banking operations
Command Pattern
Encapsulates each banking operation (create, deposit, withdraw, transfer, pass) as a separate command object with validation and execution logic.
Need to support multiple operations with different validation rules and execution logic
Separate validators and processors for each command type
// CommandValidation coordinates validators
class CommandValidation {
validateCommand(command: string): boolean {
const type = this.getType(command);
switch (type) {
case 'create':
return this.createValidator.validate(command);
case 'deposit':
return this.depositValidator.validate(command);
// ... other commands
}
}
}
// Each command has its own validator
class DepositCommandValidator {
validate(command: string): boolean {
return this.checkFormat(command) &&
this.checkLimits(command) &&
this.checkAccountExists(command);
}
}Repository Pattern
Bank class acts as a repository, abstracting account storage and providing a clean interface for account management operations.
Need centralized account storage with efficient lookups and lifecycle management
Bank repository with Map-based storage for O(1) access
class Bank {
private accounts: Map<string, Account>;
addAccount(account: Account): void {
this.accounts.set(account.getAccountID(), account);
}
getAccount(id: string): Account | undefined {
return this.accounts.get(id);
}
getAllAccounts(): Map<string, Account> {
return this.accounts;
}
removeAccount(id: string): void {
this.accounts.delete(id);
}
}Factory Method (Implicit)
Account creation is handled through processors that instantiate the correct account subclass based on the command type parameter.
Need to create different account types (Checking, Savings, CD) based on runtime input
Processor determines type and creates appropriate instance
class CreateCommandProcessor {
execute(command: string): void {
const [_, type, id, apr, balance] = command.split(' ');
let account: Account;
switch (type.toLowerCase()) {
case 'checking':
account = new Checking(id, parseFloat(apr));
break;
case 'savings':
account = new Savings(id, parseFloat(apr));
break;
case 'cd':
account = new CertificateOfDeposit(
id,
parseFloat(apr),
parseFloat(balance)
);
break;
}
this.bank.addAccount(account);
}
}Strategy Pattern
Different validation strategies for each command type, allowing runtime selection of the appropriate validation algorithm.
Each command type has unique validation rules that differ significantly
Separate validator classes implementing command-specific validation logic
// Different strategies for different commands
class WithdrawCommandValidator {
validate(command: string, bank: Bank): boolean {
// Strategy 1: Check withdrawal limits
if (account.type === 'Savings') {
return amount <= 1000; // Savings limit
}
return true; // Checking has no limit
}
}
class TransferCommandValidator {
validate(command: string, bank: Bank): boolean {
// Strategy 2: Check both accounts
return fromAccount.exists() &&
toAccount.exists() &&
fromAccount.id !== toAccount.id;
}
}Template Method (Implicit)
Account base class defines the skeleton of time passage operations, with subclasses overriding specific steps like APR compounding.
All accounts accrue APR but CD accounts need quarterly compounding
Base class provides template, subclasses override specific methods
abstract class Account {
// Template method - same for all accounts
accrueMonthlyApr(): void {
if (this.balance > 0) {
const monthlyRate = (this.APR / 100) / 12;
this.balance += this.balance * monthlyRate;
}
}
}
class CertificateOfDeposit extends Account {
// Override to compound quarterly
accrueMonthlyApr(): void {
if (this.balance > 0) {
const monthlyRate = (this.APR / 100) / 12;
// Compound 4 times (quarterly)
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
this.balance += this.balance * (monthlyRate / 4);
}
}
}
}Object-Oriented Programming Principles
This banking system demonstrates the four pillars of OOP through practical implementation
Encapsulation
Account balance and internal state are private fields, accessed only through controlled public methods that enforce business rules and validation.
class Account {
protected balance: number;
protected APR: number;
deposit(amount: number): boolean {
if (amount > 0) {
this.balance += amount;
return true;
}
return false;
}
getBalance(): number {
return this.balance;
}
}- •Prevents direct manipulation of sensitive data
- •Enforces validation rules
- •Hides implementation details
Inheritance
Checking, Savings, and CD accounts extend the base Account class, inheriting common functionality while adding type-specific behavior.
abstract class Account {
protected accountID: string;
protected balance: number;
accrueMonthlyApr(): void {
const monthlyRate = (this.APR / 100) / 12;
this.balance += this.balance * monthlyRate;
}
}
class CertificateOfDeposit extends Account {
// Override for quarterly compounding
accrueMonthlyApr(): void {
const monthlyRate = (this.APR / 100) / 12;
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
this.balance += this.balance * (monthlyRate / 4);
}
}
}- •Code reuse across account types
- •Consistent interface
- •Easy to add new account types
Polymorphism
Bank stores accounts as the base Account type, allowing method calls to dynamically dispatch to the correct subclass implementation at runtime.
class Bank {
private accounts: Map<string, Account>;
processPassTime(months: number): void {
this.accounts.forEach(account => {
// Calls the correct subclass method
account.accrueMonthlyApr();
account.deductMinimumBalanceFee();
// CD compounding happens automatically!
});
}
}- •Write generic code that works with any account type
- •Runtime flexibility
- •Extensible design
Abstraction
Complex command validation logic is abstracted into separate validator classes, each responsible for validating one command type.
class CommandValidation {
private validators: Map<string, Validator>;
validateCommand(command: string): boolean {
const type = this.getCommandType(command);
const validator = this.validators.get(type);
return validator?.validate(command) ?? false;
}
}
class DepositCommandValidator {
validate(command: string): boolean {
// Complex validation logic hidden here
return this.checkFormat(command) &&
this.checkLimits(command) &&
this.checkAccountExists(command);
}
}- •Simplifies complex operations
- •Hides implementation details
- •Easier to maintain and test
Test Coverage & Quality Assurance
Comprehensive test suite ensuring reliability and correctness
Test Suite Breakdown
Example Test Cases
APR Accrual Calculation
Verifies that annual percentage rate is correctly calculated and applied monthly
it('accrues APR correctly over time', () => {
const bank = new Bank();
const mc = new MasterControl(bank);
const commands = [
'create savings 12345678 6.0',
'deposit 12345678 1000',
'pass 1'
];
const output = mc.start(commands);
// Expected: 1000 * (1 + 0.06/12) = 1005.00
expect(output[0]).toMatch(/Savings 12345678 1005\.00 6\.00/);
});Minimum Balance Fee
Tests that accounts with balance below $100 are charged a $25 monthly fee
it('deducts minimum balance fee correctly', () => {
const bank = new Bank();
const mc = new MasterControl(bank);
const commands = [
'create checking 12345678 1.0',
'deposit 12345678 50',
'pass 1'
];
const output = mc.start(commands);
// Expected: 50 - 25 = 25.00
expect(output[0]).toMatch(/Checking 12345678 25\.00/);
});CD Quarterly Compounding
Validates that Certificate of Deposit accounts compound interest quarterly instead of monthly
it('applies quarterly compounding for CD accounts', () => {
const bank = new Bank();
const mc = new MasterControl(bank);
const commands = [
'create cd 12345678 4.0 10000',
'pass 1'
];
const output = mc.start(commands);
// CD compounds 4 times in a month
const expected = 10000 * Math.pow(1 + 0.04/12/4, 4);
expect(output[0]).toMatch(/Cd 12345678 10033\.36/);
});Testing Approach
Unit Tests
- ✓ Individual class methods
- ✓ Edge case handling
- ✓ Error conditions
Integration Tests
- ✓ End-to-end workflows
- ✓ Multi-account scenarios
- ✓ Command processing pipeline
Technical Overview
Key Features
- Three account types: Checking, Savings, Certificate of Deposit
- Full transaction support: deposit, withdraw, transfer
- Time simulation with APR accrual and fee application
- Comprehensive validation and error handling
- Transaction history tracking and audit trail
Technologies & Patterns
- Command Pattern: Separation of validation and execution
- Repository Pattern: Bank manages account storage
- Polymorphism: Account inheritance hierarchy
- Test-Driven Development: 151 passing tests
- TypeScript + React: Type-safe modern web interface